Verifying tenant income is one of the most important steps in screening renters. Without accurate proof of earnings, landlords risk late payments or even potential eviction issues. That’s why a clear, structured process is essential.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to verify tenant income — from requesting the right documents to reviewing them for accuracy. You’ll also understand why income checks matter, what red flags to watch for, and how tools like LeaseRunner’s Income Verification report can simplify the process.
By the end, you’ll know exactly how to assess a renter’s financial stability and make confident leasing decisions.
This complete guide ensures that you understand how to verify tenant income and choose the best applicants for your rental property. Before we dive into the details, here is a table of quick facts that covers the six most-searched criteria on this topic:
Why Verifying Tenant Income Matters for Landlords?
Verifying tenant income is essential for many reasons. Landlords must know that a renter can afford the rent. It also helps to reduce the risk of late payments and defaults. When you know how to verify tenant income, you can screen tenants better and build a stable rental portfolio. A clear income verification process also saves time and money in the long run.
The process of income verification is not just a formality. It provides you with rental income proof that confirms the tenant’s ability to pay. A proper review of income verification documents helps you avoid renting to someone who may not meet the financial requirements.
Additionally, landlords should combine income verification with identity proofing vs identity verification and tenant reference checks to ensure a comprehensive screening process.
6 Effective Ways to Verify Tenant Income
When you ask, "how to verify tenant income," you need to review a range of documents. Below, we list the main types of documents used for income verification.
1. Pay Stubs
Pay stubs are one of the most common documents. They show a tenant’s earnings for a given period. Many landlords ask, "How do landlords verify pay stubs?" to ensure that income is stable and the pay stub is authentic. Along with pay stubs, an income letter for apartment is useful.
An income letter from an employer confirms the tenant’s salary and job status. Together, these documents provide strong proof of income for apartment applications. If your applicant is moving due to a job change, you can also ask for an Offer Letter, which states the job’s start date and salary.
In practice, ask your applicant to provide the last two or three pay stubs. Also, request an income letter if available. These documents are a primary method for income verification for rental.
2. Bank Statements
Bank statements can provide rental income proof. They show the tenant’s deposits, spending habits, and overall financial health. Many landlords wonder, "Can a landlord check your bank account balance"?
While you must respect privacy laws, a summary or redacted bank statement can help you see the overall financial picture. These statements are a good complement to pay stubs.
You should ask for recent bank statements that cover at least one to two months. This helps you see consistent deposits and evaluate financial stability. Analyzing these statements is key to understanding their overall financial picture.
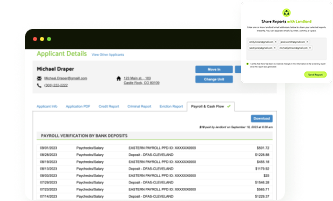
Just like with pay stubs, bank statements can be altered to qualify for your rental property. LeaseRunner’s Income Verification and Cash Flow report avoids this possibility as the report pulls real data from the applicant’s bank account directly to the landlord’s LeaseRunner account.
3. Tax Returns and 1099 Forms
Tax returns are a key part of income verification. They offer a detailed view of income over a year. For self-employed tenants or those with irregular income, tax returns and 1099 forms are essential documents. They act as proof of income for apartment applications when other documents may not suffice.
Collect at least the last two years’ tax returns and any relevant 1099 forms especially if your applicant is self-employed.. These documents help verify consistent income, especially for self-employed tenants. We recommend asking for Tax Returns as your last resort of income verification as these reports contain very sensitive information. The last thing you want is an applicant accusing you of identity theft.
You can also check guides on how to pay no taxes on rental income if tenants report rental income from other properties.
4. Rental Income Proof from Previous Properties
If a tenant has been a landlord or has rental income from other properties, you should review their rental income proof. This document shows additional income streams. It can include lease agreements from previous properties or statements from rental management companies.
After reviewing rental income proof, it is also wise to mention tools like LeaseRunner. LeaseRunner offers an Income Verification report that helps ensure all details are correct. The report checks the tenant’s pay stubs, bank statements, and other income documents. This step is vital for making sure you have accurate income verification documents.
LeaseRunner uses strict criteria to validate the information. The report confirms that all details are current and accurate. This ensures that you know exactly how to verify tenant income using the best available data.
5. Employment verification letter
An employment verification letter is a straightforward way to confirm job title, salary, and status of employment. It should be written on company letterhead and ideally signed by a manager or HR representative.
For landlords, this document provides assurance that the applicant is indeed employed where they claim and earning the stated income. It also reduces the risk of fabricated pay stubs or altered bank statements since it comes directly from the employer. In fact, many landlords use it to cross-check information already provided in pay stubs or offer letters.
When requesting this letter, be clear about what details you need. At minimum, ask for:
- Employment start date
- Position or job title
- Current annual or monthly salary
- Employment status (full-time, part-time, or contract)
This document works best in combination with pay stubs or bank statements to provide a complete picture of both job security and actual earnings.
6. Statements for other income
Not all tenants rely solely on wages. Many have alternative or supplementary income sources that can strengthen their rental application. Landlords should request official documentation to verify these streams, such as:
- Social Security benefits: Tenants receiving Social Security can provide official award letters or bank statements showing consistent deposits.
- Pension or annuity distributions: Retirees or tenants with pensions/annuities should submit statements from the plan administrator.
- Workers’ compensation: Individuals receiving workers’ compensation should provide award letters or payment history.
- Court-ordered payments (e.g., alimony or child support): Documentation such as court orders or direct deposit records can serve as income verification documents, showing legally mandated payments that can supplement a tenant’s income.
- Unemployment statements: For tenants temporarily out of work, unemployment benefit letters or payment records demonstrate an official income source. Landlords can use this as part of tenant income verification methods to ensure the renter can meet rent obligations.
When reviewing these statements, check for consistency in payment amounts and frequency. This type of documentation is particularly valuable for retirees, individuals recovering from injury, or tenants in transition between jobs.

Step-by-Step Guide to Verify Tenant Income
This section explains a clear process for verifying tenant income. We base this guide largely on LeaseRunner’s Income Verification process. By following these steps, you will learn how to verify tenant income and screen applicants accurately.
Step 1: Request Appropriate Income Verification Documents
Begin by collecting the key documents we covered earlier: pay stubs, bank statements, tax returns, and employment verification letters. Each adds a layer of proof: pay stubs confirm earnings, bank statements show deposits, and letters verify job stability.
Also, ask for at least two to three recent pay stubs, a current bank statement, and an employment letter if possible. Tools like LeaseRunner simplify this step with secure requests and checklists, ensuring you start the process with reliable information.
Step 2: Cross-Check Information Provided
Once you receive the documents, compare the details. Check the figures on the pay stubs against the bank statements. See if the income matches the tax returns. This process shows you how to verify tenant income reliably. Cross-checking helps you catch errors and verify that the applicant truly earns what they claim.
Step 3: Perform Tenant Screening and Credit Checks
A thorough income verification process includes credit checks. LeaseRunner and similar tools offer tenant screening services. These services help you see if the applicant has a history of timely payments.
By running a credit check, you add another layer of security to your income verification. This step is vital when you need to know how to verify tenant income and assess financial reliability.
Step 4: Follow Up with the Employer or Income Source
If any details are unclear, contact the employer. Verify that the income letter is authentic. Ask for clarification on any discrepancies. Follow-up ensures that you complete the income verification process accurately. This final step confirms that the information provided is correct and that you know how to verify tenant income effectively.
How Is Rental Income Eligibility Calculated?
Rental income eligibility is typically measured by comparing a tenant’s income against the cost of rent. Landlords and property managers use several methods to determine whether an applicant earns enough to cover monthly housing expenses:
- Rent-to-Income Ratio: The most common standard requires that rent should not exceed 30–40% of the tenant’s gross monthly income. For example, if the monthly rent is $1,000, the tenant should have a gross income of at least $3,000–$4,000 per month.
- Minimum Income Multiples: Some landlords set a rule that income must equal 2 to 3 times the monthly rent. This simplifies screening but may exclude applicants with strong savings or additional financial resources.
- Adjusted Net Income: For applicants with multiple income streams, landlords may calculate net income by subtracting taxes, insurance, or business expenses to assess what’s actually available for rent.
- Stability of Earnings: Beyond raw numbers, landlords look for steady employment or recurring deposits over time. Consistency across pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements helps prove that income is reliable.
These calculations provide a baseline, but landlords often combine them with credit check and rental history to get a full picture of affordability.
The Risks of Fake Pay Stubs
While pay stubs are one of the most common documents used to verify income, they are also among the easiest to falsify. Accepting fake pay stubs carries serious risks:
- Financial Loss: A tenant with inflated income may quickly fall behind on rent, leaving the landlord with unpaid balances and potential eviction costs.
- Legal Liability: Submitting fraudulent documents can constitute fraud or forgery. If discovered, it may involve legal proceedings or financial disputes.
- Time and Expense: Detecting and addressing fraudulent documents often requires additional screening tools, third-party services, or even legal support, which increases operational costs.
- Reputation Risks: For property managers, approving tenants based on false documents can damage credibility with owners and future renters.
Because of these risks, landlords should never rely on a single document when verifying tenant income.
How Landlords Can Spot Fake Proofs of Income?
Spotting fraudulent income documents is critical to protecting rental property. Here are several techniques landlords can use:
- Check Formatting and Layout: Real pay stubs follow consistent patterns. Look out for unusual fonts, spacing issues, blurry logos, or missing details.
- Review Numerical Data: Pay stubs that use rounded figures, lack deductions (taxes, insurance, retirement), or show inconsistent earnings are red flags.
- Verify Employer Information: Cross-check company addresses, phone numbers, and emails. If the contact information is untraceable or unverifiable, the document may be fake.
- Confirm Dates and Pay Periods: Payment cycles should align with standard pay schedules. Odd or repetitive dates suggest tampering.
- Cross-Reference Other Documents: Compare pay stubs with bank statements, W-2s, or tax returns to ensure deposits match reported income.
- Use Technology: Fraud-detection tools and third-party services, such as LeaseRunner or Snappt, can identify altered or fabricated documents quickly.
By combining visual checks with third-party verification, landlords can greatly reduce the risk of accepting false proofs of income.
Is There a Way to Verify Someone’s Income Without Documents?
Not all tenants can provide traditional income documents like pay stubs or tax returns. In such cases, landlords have alternative methods to verify earnings:
- Third-Party Income Verification Services: Platforms like LeaseRunner can securely access bank transaction data (with tenant consent) to confirm actual cash flow.
- Direct Employer Contact: Contacting the employer directly can validate job status and salary details without relying on a tenant-provided letter.
- Rental History Checks: Consistent on-time payments to past landlords indicate that an applicant has a track record of meeting housing obligations.
- Bank Account Reviews: Even without formal documents, bank statements showing regular deposits can serve as proof of steady income.
- Credit Reports: A strong credit history often reflects financial responsibility, even if traditional income documents are unavailable.
These methods should be used carefully, respecting privacy and legal requirements. When combined, they help landlords make informed decisions even in cases where standard documentation is missing.

Common Issues When Verifying Tenant Income (And How to Solve Them)
Even with a clear process, you may face challenges. Here are common issues and practical solutions.
- Incomplete Documents: Sometimes, tenants do not provide all the required documents. Ask for any missing items. A complete set of income verification documents is key. Explain why these documents are needed.
- Discrepancies in Figures: You may find differences between pay stubs, bank statements, and tax returns. In such cases, ask for clarification. Contact the tenant and, if needed, their employer. Cross-checking helps resolve these issues.
- Outdated Information: If the documents are not recent, ask for updated copies. For instance, if you see an old pay stub, ask for a new one. Always check that the documents are current so you know how to verify tenant income reliably.
- Irregular Income Patterns: For tenants with irregular income, review last 2–3 months paystubs, tax returns, and bank statements to confirm stability. This gives you a better idea of their earning patterns. Use multiple documents to form a complete picture.
- Privacy Concerns: Some tenants worry, "Can a landlord check your bank account balance"? Ensure you respect privacy. Ask for redacted statements if necessary or use LeaseRunner’s Income Verification report.. Explain that your goal is to verify overall income, not to view every transaction.
By addressing these issues, you can streamline the process and learn exactly how to verify tenant income without confusion.
Bottom Line
Knowing how to verify tenant income is essential for landlords. The process protects your investment and helps you choose reliable tenants. Using documents such as pay stubs, bank statements, tax returns, and income letters gives you strong rental income proof. These steps ensure you can evaluate financial stability and truly understand a tenant’s financial health.
By following this guide from the LeaseRunner team, you will learn how to verify tenant income in a clear, step-by-step manner. The methods in this article protect your property and help build a stable rental portfolio. Use these guidelines for every rental application for California and ensure that each applicant meets your income requirements.
FAQs
Q1. What is the best way to verify tenant income?
The best way is to request the Income Verification and Cash Flow report and reference it with other income verification documents such as pay stubs, income letters, bank statements, and tax returns if needed. This combined evidence offers strong rental income proof.
Q2. Can I check the applicant’s bank account balance?
Landlords may ask for the Income Verification and Cash Flow report or redacted bank statements to confirm deposits.
Q3. How do landlords verify pay stubs?
Landlords review recent pay stubs and compare them with bank statements. This process shows clear evidence of income.
Q4. How do I verify income for rental property if the tenant is self-employed?
In that case, ask for tax returns and 1099 forms along with bank statements or tax returns This shows clear proof of income for apartment applications.
Q5. Do Landlords Ask for Tax Returns?
Yes, landlords may request tax returns as part of verifying a tenant’s income, especially if the applicant is self-employed or has irregular income. Tax documents like W-2s, 1040s, or 1099 forms provide reliable proof of income for apartment applications and help landlords evaluate financial stability.