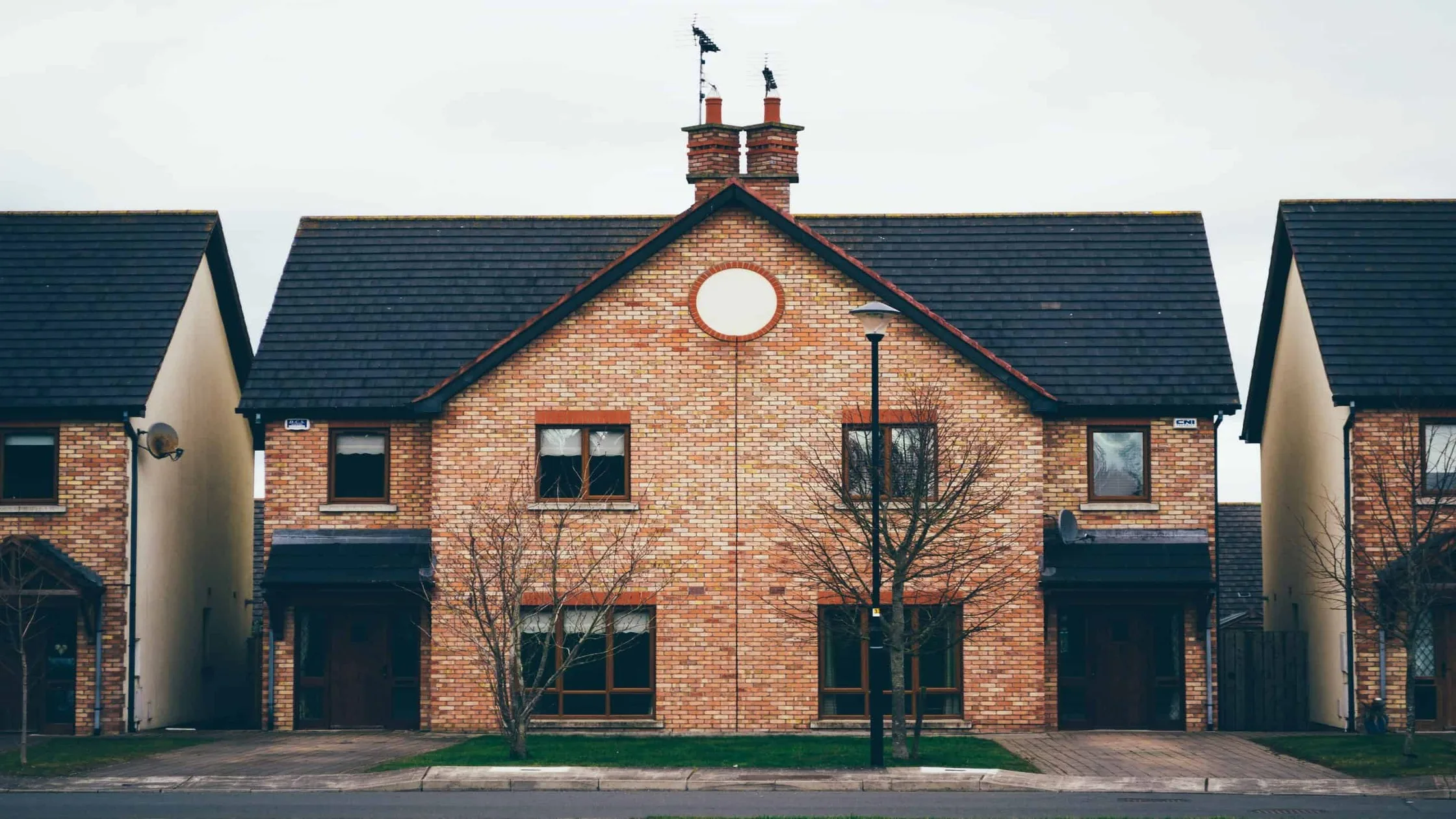
So, what is house hacking? It’s a simple concept with powerful results: live in one part of a property and rent out the other. That extra space from a duplex or a basement unit can help cover the mortgage or even generate profit.
In this article, we will provide you with a house hacking guide to combat rising housing costs and build wealth without waiting for the perfect time to invest.
What is House Hacking?
House hacking is a strategy that blends homeownership with real estate investing. It involves living in one part of a property while renting out the other parts to generate income.
This can be done with a multi-unit property, a single-family home with extra bedrooms, or even a basement or garage apartment.

The goal is to use the rental income to offset housing expenses, build equity faster, and potentially live for little to no out-of-pocket cost.
It's important to note that house hacking is very different from phrogging (people secretly living in someone else’s home without permission). While phrogging is illegal and invasive, house hacking is completely legitimate, transparent, and mutually beneficial when done with proper agreements and tenant screening.
How Does House Hacking Work?
Now that you’ve learned what house hacking is, next is how it works.
House hacking works by combining three financial elements: ownership, occupancy, and rental income. A person buys a property, lives in one unit or portion, and rents out the rest. The rental income can help cover the mortgage, utilities, and other housing costs.
This strategy turns a home into an asset that produces cash flow. Instead of paying a full mortgage out of pocket, a portion may be covered by tenants. Beyond monthly savings, house hacking can also offer long-term benefits like property appreciation, tax deductions, and leverage for future investments.
How Much Money Do You Need to Start House Hacking?
The amount needed to start house hacking depends on the property type, location, and house hacking loan choice.
- Some financing options, like FHA loans, require as little as 3.5% down for properties with up to four units.
- VA loans offer zero-down financing for eligible buyers.
- Conventional loans may require 5–20% down.
It’s important to budget for closing costs, initial repairs, and cash reserves. Starting with $10,000–$30,000 is common, though some manage to begin with less by choosing smaller properties or creative loan programs.
4 Types of House Hacking Strategies
Some methods are more hands-on, while others are more passive. Here are four of the most common and effective house hacking strategies to consider.
1. Live in One Unit, Rent Out the Rest
This is the classic house hacking setup and one of the easiest to manage. It usually involves buying a small multi-family property like a duplex, triplex, or fourplex. The owner lives in one unit and rents out the others.
This setup allows for clear separation between living spaces and tenants. It also makes financing easier, since lenders often allow borrowers to count projected rental income when applying for a loan. With the right numbers, it’s possible to cover the entire mortgage with rental income from the other units.
2. Rent Out Extra Bedrooms in a Single-Family Home
A more accessible strategy! This approach involves renting out spare bedrooms in a home, ideal for college towns, major cities, or areas with a lot of young professionals.
It requires some shared living and more interaction with tenants, but the startup costs are typically lower since it only involves purchasing a single-family home. Many owners use this as a stepping stone: starting small, building equity, and eventually leveling up to a multi-unit property.
3. House Hacking with an ADU (Accessory Dwelling Unit)
Adding or purchasing a home with an ADU offers a great middle ground between privacy and profitability. The main home remains a private living space, while the ADU serves as a separate rental unit.
This strategy works well in cities that support ADU development through zoning changes and housing incentives. ADUs can be rented long-term, used as short-term rentals, or even house family members while reducing costs.
4. Short-Term Rental House Hacking (Airbnb, VRBO)
Instead of signing year-long leases, some house hackers use platforms like Airbnb or VRBO to rent out part of their home for short stays. Short-term rentals often bring in higher monthly income than long-term tenants. However, they require more effort: cleaning, guest communication, and managing bookings. Reviews, hospitality, and city regulations all play a big role in success here.
How to House Hack as a Beginner?

The process may sound complex at first, but breaking it down into clear steps makes it easier to navigate how to house hack as a total newbie.
Step 1: Choose the Right Property Type
The best house hacking properties offer separate living spaces and strong rental potential. Duplexes, triplexes, and fourplexes are popular choices, but single-family homes with finished basements, garages, or extra bedrooms can work just as well.
Zoning laws and layout play a big role here.
- Zoning laws determine whether you’re legally allowed to rent out parts of your home. For example, some areas prohibit basement rentals or require special permits for multi-unit use
- Layout affects privacy and livability for both you and your tenants. Say, having a separate entrance or a private bathroom can really improve how attractive and usable the space is for tenants.
Step 2: Explore House Hacking Loan Options
Financing is a part of what is making house hacking affordable. FHA loans are popular for house hacking, especially for 2–4 unit properties, offering low down payments (as low as 3.5%) and flexible credit requirements.
VA loans allow qualifying military members to buy multi-unit properties with no money down. Conventional loans also work, especially for those with strong credit and some savings. Many first-time buyers combine these loan options with grants or assistance programs to lower their upfront costs.
Step 3: Crunch the Numbers
Before buying, it’s important to run the numbers. Start by estimating the monthly mortgage payment, including property taxes and insurance. Then calculate potential rental income from the additional units or rooms.
Subtract operating costs like maintenance, vacancy allowance, and utilities to get a realistic picture of cash flow. Building in reserves for emergencies or repairs adds a layer of safety.
Step 4: Prepare to Be a Landlord
Renting part of a home comes with responsibilities, like understanding local landlord-tenant laws, drafting clear leases, and screening tenants carefully. Setting clear expectations with house rules and boundaries makes shared living situations smoother.
Never rented out a property before? Check out this helpful guide on renting out a house for the first time to get familiar with tenant screening, lease agreements, and what to expect as a landlord.
Legal & Zoning Rules You Should Know Before House Hacking

House hacking can be a smart way to earn income, but it’s important to play by the rules.
Zoning Laws for Multi-Unit and ADU Properties
Zoning laws determine what types of buildings are allowed in certain neighborhoods. In some areas, duplexes and triplexes are permitted; in others, only single-family homes are legal. So, before buying a multi-unit or adding an ADU, be sure to check your local city or county planning department website or speak with a zoning officer for property-specific details.
Some cities are actively encouraging ADUs and gentler density by relaxing restrictions. Others still have tight rules about separate entrances, parking spaces, or minimum lot sizes. Always verify what’s legally allowed before assuming potential rental income.
Understanding zoning is also important when calculating ARV (After Repair Value) in real estate. For example, if zoning restrictions prevent you from adding square footage or converting a garage into a rental unit, it can limit the property's future value and reduce your expected return on investment.
Local Rental Laws That Apply to Owner-Occupied Properties
Even for owner-occupied homes, rental laws still apply. Some cities limit the number of unrelated tenants per home, require rental licenses, or mandate inspections. Noise ordinances, occupancy limits, and fair housing laws must also be followed.
In most cases, once someone moves in, even into a spare room, they gain legal protections. Having a clear lease and following proper eviction processes protects both the landlord and the tenant.
Rules You Must Follow for Airbnb or Short-Term Rentals
Short-term rentals often fall under a different set of regulations. Some cities require a business license, proof of owner-occupancy, or even caps on how many nights per year a space can be rented.
Other common requirements include fire safety inspections, tax registration, and guest limits. In some neighborhoods or HOAs, short-term rentals may be banned altogether.
Therefore, always check with your local government or HOA to make sure your setup is compliant before listing your space.
Benefits of House Hacking for Landlords & Aspiring Homeowners
What is house hacking without its benefits for investments? House hacking turns a personal residence into a financial asset. It brings real benefits for those just starting their real estate journey or aiming to grow it.
Reduce or Eliminate Your Housing Costs
One of the biggest perks of house hacking is dramatically lowering monthly housing costs. Renting out a portion of the property brings in steady income, which can be used to pay the mortgage, taxes, insurance, and utilities.
Many people find themselves living with little to no housing expenses, opening up funds for other priorities like saving or investing. In some situations, rental income surpasses all housing costs, transforming the property into a profit generator.
Build Equity and Financial Independence
Each mortgage payment helps build equity in the property. That equity becomes a valuable asset that can be tapped into later for home improvements, future investments, or emergency funds.
House hacking also accelerates the journey toward financial independence. Instead of waiting years to buy an investment property, this strategy allows people to start small, learn the ropes, and benefit from income and appreciation at the same time.
Real Estate Tax Advantages
Owning a property that also generates rental income opens the door to a range of tax benefits. A portion of mortgage interest, property taxes, depreciation, and repair costs can often be written off against rental income.
Even things like maintenance supplies, utilities (for shared spaces), and part of the home office setup may qualify as deductions. These benefits help lower taxable income, making the investment more efficient in the long run.
Step Toward Scaling Your Investment Portfolio
House hacking offers hands-on experience with property management, tenant relationships, and cash flow analysis, all while living in the property.
This real-world education builds confidence and credibility. Many successful investors started with one house hack and leveraged it into a full portfolio over time.
House Hacking vs Traditional Real Estate Investing
Both house hacking and traditional real estate investing can lead to long-term wealth, but the paths look a little different.
For House Hacking
For Traditional Investing
So, which one is more suitable for you?
House hacking tends to be a smart fit for first-time buyers, those with limited capital, or anyone looking to reduce their housing costs while easing into real estate.
On the other hand, traditional real estate investing often suits those with more capital to deploy, a higher risk tolerance, or experience in property management and financing.
But you can definitely do both! Many investors start with house hacking, build equity, learn the ropes, and then use that experience to expand into traditional investing. Some even continue living in one property while managing others, blending both strategies to build a well-rounded portfolio.
Housing Arbitrage: A Twist on House Hacking

There’s another way to earn rental income without buying a home. It’s called housing arbitrage, and it flips the script on how real estate cash flow can work.
What Is Housing Arbitrage and How Does It Work?
Housing arbitrage is a strategy where someone rents a property long-term from a landlord, then re-rents it short-term on platforms like Airbnb or VRBO. The key is negotiating a lease that allows it, then earning more from guests than the original rent.
Unlike what house hacking is and how the strategy works, housing arbitrage doesn’t involve owning the home. It’s about controlling a property through a lease and profiting from the difference between rent and rental income.
Pros and Cons of Arbitrage vs Ownership
Pros of housing arbitrage:
- No large down payment or mortgage needed
- Faster entry point—especially in high-demand markets
- Scalable with the right systems and agreements
Cons of housing arbitrage:
- No equity or long-term appreciation
- Requires clear landlord permission and local legal compliance
- More exposure to income volatility in short-term rental markets
Compared to house hacking, arbitrage is more flexible but less stable. There's potential for strong cash flow.
Who is House Arbitrage Best For?
Housing arbitrage is often ideal for people who:
- Have strong hosting, hospitality, or property management skills
- Don’t have the capital for a down payment
- Are looking for a faster, cash-flow-focused strategy
- Are comfortable operating within short-term rental rules and landlord agreements
It’s not a passive approach, but for the right person, it offers a creative and relatively low-cost way to break into real estate income without buying a property upfront.
Bottom Line
So, what is house hacking? Simply put, it’s living in a property while renting part of it out. The benefits can be huge: reduced costs, income potential, and a low-barrier entry into the world of real estate investing.
We hope this guide has helped you lots. Check out the LeaseRunner blog for more in-depth tips and strategies on house hacking and other real estate topics!
FAQs
Q1. How does hacking actually work?
House hacking is a smart real estate strategy that allows you to combine your living space with an income-generating investment. The idea is simple: you purchase a property, live in one portion of it (like a unit, room, or floor), and rent out the remaining space. This setup allows you to collect rental income from tenants. At the same time, you’re building equity in the property and gaining hands-on experience as a landlord.
Q2. What are some key real estate terms 101 I should know before house hacking?
Here are a few basics:
- Equity – The portion of the property you truly own (market value minus your mortgage balance).
- Cash Flow – The money left after paying expenses (rent income minus mortgage, taxes, insurance, etc.).
- Cap Rate – A formula used to estimate return on investment: (Net Operating Income ÷ Property Value).
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) – How much you’re borrowing compared to the property’s value.
- House Hack – A strategy where you live in a property and rent out part of it to offset costs.
Q3. Do I need to be a landlord to start house hacking?
Technically yes, but you don’t need experience to start. You’ll be responsible for typical landlord duties like collecting rent, handling basic maintenance, and addressing tenant concerns. It’s important to be prepared for these responsibilities and to treat your tenants professionally. With a little planning and a willingness to learn, house hacking can be a manageable and highly rewarding way to break into real estate.