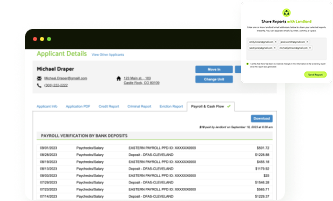
Understanding the rent-to-income ratios is crucial for both renters and landlords. Knowing the appropriate rent-to-income proportion will enable you to make wise, sustainable choices, whether you are looking for your new apartment or screening possible renters.
This tutorial looks at why it is important for financial health and property management, how to calculate the ratio, and what percentage of income should go toward rent. Don’t hesitate any longer, let's scroll down!

What Is a Rent-to-Income Ratio?
The rent-to-income ratio is the percentage of a tenant’s gross monthly income spent on rent. Landlords use it while screening potential tenants to check if they can realistically afford the rental costs. At the same time, tenants use it to check if their housing fits within their budget.
A good rent-to-income ratio is generally 30% or less of a tenant’s gross monthly income — a guideline often called the “30% Rule.” According to Chase Bank, this benchmark helps tenants leave enough room in their budget for essentials, savings, and emergencies. Landlords usually look for proof of income during the application process to confirm this ratio. Some also require tenants to earn at least 3x the rent as an extra safeguard.
Meanwhile, the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) considers households spending more than 30% of their adjusted income on rent as rent-burdened, and those spending over 50% as severely rent-burdened. Although landlords typically use this standard during tenant screening, they may accept higher ratios—between 30% and 45%—if an applicant’s overall financial profile is strong and justifies flexibility, especially when learning how to screen Section 8 tenants.
Quick Facts Table About Rent/Income Ratio
How to Calculate Your Rent-to-Income Ratio?
As mentioned earlier, the common benchmark is 30%. With that in mind, there are two simple ways to calculate your rent-to-income ratio:
- Method 1: Checking a tenant’s rent-to-income ratio
- Method 2: Calculating the minimum income required
Here’s how it works in practice
1. Checking a tenant’s rent-to-income ratio
Apply this formula:
This formula shows what percentage of a tenant’s income would go toward rent. Landlords use it when they want to assess affordability and make sure rent won’t place too much financial strain on the tenant. It’s most useful during tenant screening, as it quickly confirms whether applicants meet the standard 30% benchmark.
For instance, a tenant applying for a property with:
- Monthly rent = $1,800
- Tenant’s gross monthly income = $6,000
- Plugging the numbers into the formula → Ratio = (1,800 ÷ 6,000) × 100 = 30%
That means the tenant is spending exactly 30% of their income on rent — right at the standard benchmark. In this case, the tenant would qualify.
2. Calculating the minimum income required
The formula looks like this:
This formula flips the perspective by showing how much income a tenant should earn to qualify. Landlords often use it when setting clear application criteria (“must earn 3x the rent”) to simplify the screening process. It’s especially helpful when advertising rental listings or explaining upfront requirements to potential tenants.
For example, let’s say
- Monthly rent for a unit = $2,500.
- Using the formula, you multiply → Required Gross Monthly Income = 2,500 × 3 = $7,500.
This tells you that a tenant should earn at least $7,500 per month to meet the income requirement. If they earn less, landlords might ask for extra assurance, like a co-signer, a guarantor, proof of income, or evidence of additional savings.
Rent-to-Income Ratios: Guidelines and Alternatives
The 30% Rule: A commonly cited guideline
The "3x rule" is a frequent and straightforward memory aid for rent-to-income ratios. But the question is “Why should the proportion of income allocated to rent be 30%? The idea is simple—it leaves room for savings, daily expenses, and emergencies, while also giving landlords a quick way to judge if a tenant can reasonably afford rent.
There are a few variations on this rule:
- 2.5x Rent: In high-cost markets, some landlords lower the requirement to 2.5x income.
- 28–30% of Gross Income: Another version is to keep rent at or below 28–30% of gross monthly income.
What If the 30% Rule Doesn’t Fit?
The rent-to-income ratio is a handy starting point, but it doesn’t tell you everything about a tenant’s finances. To really see the bigger picture, landlords can lean on a few alternative considerations alongside it:
Why Rent to Income Ratio Is Important ?
For landlords, the rent-to-income ratio is a reliable tool for screening potential tenants. It helps assess whether applicants can realistically meet their rent obligations, lowering the risk of late or missed payments and ensuring a stable rental relationship. Combined with a credit check, it gives landlords a clearer picture of a tenant’s financial reliability. The ratio also supports smarter decisions when evaluating rental property cash flow and setting sustainable rental terms.
For renters, the ratio works as a budgeting guide. By following the 30% rule, tenants can avoid financial strain and balance rent with other expenses. This becomes especially important when dealing with rising housing costs, such as a month-to-month rent increase in California.
3 Key Factors affects rent-to-income ratio
As a landlord, you know the numbers don’t always speak for themselves. Here are the biggest factors that influence how reliable a rent-to-income ratio truly is.
1. Income Level
Obviously, a tenant’s income is the most direct factor affecting their rent-to-income ratio. A tenant with higher income will naturally have a healthier rent-to-income ratio, making it less likely they’ll struggle to pay on time. But with lower-income tenants, sticking to the 30% rule or requiring them to find a roommate can make the arrangement more secure for you.
2. Rent Prices and Location
The rent-to-income ratio can look very different depending on where a tenant lives.
- Urban vs. Suburban: In high-cost cities like Toronto or Miami, tenants may spend 35–40% of their income on rent, with Miami reaching as high as 54.9%. Although these figures are well above the 30% rule, strong infrastructure and reliable public transit often help balance out the higher costs.
- Rural Areas: Conversely, living in a rural area like Knoxville, renters may spend as little as 8.2% of their income on rent. Many rural areas show a similarly lower rent-to-income ratio because housing demand is weaker and rents are cheaper
So whether a tenant is paying above or below 30%, that can still be alright. The 30% rule isn’t a standard for every case, especially in markets with rent-stabilized or rent-controlled regulations. As a landlord, being flexible and looking at the bigger picture will give you a clearer sense of tenant affordability.
3. Other Financial Obligations
A clean rent-to-income ratio doesn’t always guarantee a tenant can comfortably afford your property. Debts like student loans, car payments, or credit card balances can stretch their budget thin. Family responsibilities or big savings goals can also limit what they can realistically pay each month. For landlords, this is why pairing the ratio with a credit check or reviewing additional financial details is so important.

What Are the Minimum Rent Requirements for Renting an Apartment?
If you are a landlord, you may wonder, "How much should a tenant make to afford rent"? You can roughly estimate by tripling the rent. Landlords have to establish minimum income requirements so that tenants may pay their rent.
The most generally accepted ratio is that a tenant's gross monthly income should be between 2.5 and three times their rent. This enables landlords to assess candidates and lower the possibility of evictions or unpaid bills.
More importantly, using this estimate will enable landlords to be certain that their renters have sufficient income to afford additional living expenses as well as rent. They can also rely on this information to decide how to fix the rent fees reasonably and legally.
In certain affordable areas, however, landlords may accept a much smaller income multiplier, perhaps 2.5x. Still, the 3x rule is the industry benchmark as it keeps a balance between renter affordability and landlord protection.
Screen tenants by verified income ratios—so you lease faster, smarter, and without late-payment surprises.

Know Who Can Really Afford Your Rent
How Rent-to-Income Ratios Impact Your Renting Decision
For Renters: How Much Rent Can You Afford?
One of the greatest strategies to create a reasonable budget and stay free from financial stress is knowing your rent-to-salary ratio. Once your rent-to-income ratio exceeds 30%, you may find it difficult to manage problems, save for the future, or meet other expenses. Therefore, professionals advise that the perfect rent-to-earnings ratio is either 30% or less.
For Landlords: Assessing Tenant Risk
To find out whether a renter can pay the rent, landlords use the rent-to-income ratios. A smaller percentage indicates that the renter is less prone to overlook payments. Most landlords are usually looking for a rent-to-gross salary ratio between 30% and 33%. Their screening procedure revolves around this heavily.
Although landlords could also consider credit scores and other debts when doing standard tenant screening, the income-to-rent ratio is still the main tool for determining if a renter would be a suitable match. It enables landlords and tenants to make wise decisions and steer clear of upcoming issues.
Can Rent-to-Income Ratios Help in Real Estate Investment Decisions?

Absolutely. The rent-to-income ratio is a useful indicator for real estate investors evaluating the financial situation of their tenant pool and the affordability of their holdings.
Then, what is a good income-to-rent ratio? Properties that attract tenants with a 30% or lower ratio are less likely to experience turnover or missed payments.
Investors use this estimation ratio to compare different markets, set competitive rents, and reduce vacancy risk. Besides, lenders as well as renters will also find properties with a good rent-to-income percentage appealing.
Benefits of Using Rent-to-Income Ratios
When it comes to tenant screening, the rent-to-income ratio is one of the most reliable ways to measure rental affordability and ensure both you and your tenants stay financially secure.
- Quick screening: Helps landlords quickly see if tenants can realistically afford the rent based on their gross monthly income and properly verify tenant income.
- 3x rent rule: The widely accepted guideline that a tenant should earn at least 2.5 - 3 times the rent makes it easier to set minimum rent requirements and avoid rent-burdened situations.
- Lower risk of missed payments: Reduces the chance of late rent or past-due rent notices, protecting your rental property cash flow and limiting evictions.
- Fair rent pricing: Guides landlords in setting rent levels that align with local housing costs and tenant income ranges.
- Stronger tenant retention: Attracts financially secure renters, cutting tenant turnover and keeping your property profitable long-term.
- Better investment decisions: By tracking the rent-to-income ratio, property owners or landlords can quickly gauge the financial health of their tenant pool and the affordability of their rentals. Properties where tenants keep the ratio at or below 30% tend to be more stable — with fewer missed payments, lower turnover, and stronger long-term returns. This also makes the property more appealing to both tenants and lenders, especially if you’re planning to refinance or grow your portfolio.
Limitations of Rent-to-Income Ratios
That said, the ratio should never be the only factor you rely on when evaluating tenants.
- Doesn’t show the full picture: Ignores other debts, childcare, or fluctuating income, which also impact rental affordability.
- Market differences: In high-cost cities, many tenants will exceed the 30% rule, while in lower-cost markets the ratio may look safe but still miss other financial risks.
- Not stand-alone: Works best when combined with a tenant background screening, rental history, and proof of income for a fuller picture of tenant reliability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Rent-to-Income Ratios
If you’ve been using the rent-to-income ratio but still struggle with late payments or unreliable tenants, chances are you might be running into a few common mistakes.
Using Net Instead of Gross Income
One of the most frequent mistakes is calculating the ratio based on net income rather than gross income. Since net income excludes taxes and deductions, it understates affordability and can make tenants look less qualified than they actually are. Always rely on gross (pre-tax) income for accuracy.
Ignoring Other Debts
The rent-to-income ratio only looks at rent compared to income, but it leaves out other big expenses like student loans, credit cards, or car payments. So even if a tenant’s ratio looks safe, they might still be stretched too thin if they’re carrying heavy debt. That’s why it helps to also check their debt-to-income ratio along with the rent-to-income ratio to get a clearer picture of their real financial situation.
Setting the Bar Too High or Low
The “3x rent” rule is a solid industry guideline, but applying it too rigidly might cause you to miss out on good tenants. On the other hand, being too flexible could put you at risk of missed payments. The key is finding the right balance between keeping rent affordable for tenants and protecting your property income.
Not Adjusting for Local Markets
As mentioned, the ideal rent-to-income ratio can vary significantly by location due to differences in the cost of living and average income levels. A 30% ratio might be standard in one area, but may need to be adjusted higher (e.g., 35-40%) in expensive cities or lower in more affordable areas.
Overlooking Roommates or Combined Incomes
For shared rentals, landlords sometimes evaluate applicants individually rather than as a group. In reality, the combined gross income of all tenants provides a clearer picture of affordability and reduces the risk of payment issues.
Violating Fair Housing Law
Apply rent-to-income criteria consistently to all applicants and avoid any form of discrimination. According to the NFHA, you can ask questions to confirm eligibility, but never those that reveal protected characteristics like race, religion, or family status.
What’s Next for Rent-to-Income Ratios?
Ever wonder if the rent-to-income ratio will keep holding up as the gold standard for measuring affordability? The truth is, it’s changing — shaped by shifts in the economy, housing policies, and local market realities.
After peaking in 2022, the national RTI has started to cool down thanks to slower rent growth and rising wages. But don’t let that fool you, according to : in high-demand coastal cities, ratios are still stretched thin because of limited housing supply, while more affordable regions are seeing healthier numbers, according to the U.S. Department of the Treasury (.gov).
Add to that the impact of new regulations, and the picture gets even more complex. Some policies are meant to make housing more affordable, but others may unintentionally drive rent higher. That’s why for landlords, the RTI ratio remains a useful benchmark — but it’s not a crystal ball. Pairing it with context like debt levels, income stability, and market trends will give you a much clearer sense of tenant affordability.
Moving Forward With LeaseRunner
At LeaseRunner, we know how important it is for landlords to have confidence in their tenant screening process. That’s why we make it simple to go beyond the rent-to-income ratio. With our platform, you can quickly verify tenant income, run a full tenant background screening and even streamline your rent collection process.
Whether you’re managing one unit or an entire portfolio, having the right data at your fingertips helps you protect your investment and attract reliable tenants. If you’re ready to take the next step, LeaseRunner gives you the tools to screen smarter and manage with peace of mind.
Final Thoughts
The rent-to-income ratio is a simple yet powerful tool for making informed rental decisions. For renters, it answers the question, “What percentage of income should go to rent?” For landlords, it helps set minimum rent requirements and screen tenants effectively.
Following the industry standard of 30% ensures both parties are protected from financial strain. Use the rent-to-income ratio formula to guide your choices, and always consider the broader financial context for the best results.
FAQs
Q1. What percentage of income should go to rent?
Usually, rent should be limited to around thirty percent of your total monthly income. That will still leave money for food, bills, savings, and any unexpected needs.
Q2. What is a good income-to-rent ratio?
Aim for an income-to-rent ratio of at least 3:1. In practice, that means earning three times your rent each month before taxes. These criteria are used by landlords a lot to determine if someone can comfortably pay the rent.
Q3. How do I calculate my rent-to-income ratio?
First, divide your rent each month by your pre-tax income. You will then obtain the outcome by first multiplying that figure by 100.
For example, $1,200 rent ÷ $4,000 income = 0.30 → 0.30 × 100 = 30%.
Q4. What are the minimum income requirements for renting an apartment?
Typically, landlords want tenants to make at least 2.5–3 times the rent. This buffer gives them confidence that you can cover the rent even if something unexpected comes up.
Q5. How much should a tenant make to afford rent?
Use the 3× rule and multiply the rent by three. If you have to pay $2,000 for rent, for example, you should aim for around $6,000 in monthly gross income. This helps you to keep your stress down and your budget in line.